Get best WooCommerce Plugins > Instagram stands out among tons of social media platforms as…
How to Install WordPress in a Subdirectory (Step by Step)

Do you want to install WordPress in a subdirectory? Installing WordPress in a subdirectory allows you to run multiple WordPress instances under the same domain or even a subdomain name. In this article, we will show you how to install WordPress in a subdirectory without affecting the parent domain name.
Subdomain vs Subdirectory? Which One is Better for SEO?
Normally, you would want to start a WordPress website on its own domain name (for example, wpbeginner.com). However, sometimes you may want to create additional websites on the same domain name.
This can be done by either installing WordPress in a subdomain (http://newebsite.example.com) or as a subdirectory (http://example.com/newwebsite/).
One question that we get asked is which one is better for SEO?
Search engines treat subdomains differently from root domain names and assign them rankings as a totally different website.
On the other hand, sub-directories benefit from the domain authority of the root domain thus ranking higher in most cases.
An easier way to create separate WordPress sites in both subdomain or subdirectory is by installing WordPress multisite network.
However, if you want to keep two websites managed separately, then you can install different instances of WordPress.
That being said, let’s take a look at how to install WordPress in a subdirectory.
Step 1. Create a Subdirectory under The Root Domain Name
First you need to create a subdirectory or folder under your root domain name. This is where you will install WordPress files.
Connect to your WordPress hosting account using a FTP client or File Manager in cPanel.
Once connected, go to the root folder of your website. Usually it is the /public_html/ folder. If you already have WordPress installed in the root folder, then you will see your WordPress files and folders there.
Next, you need to right click and select ‘Create new directory’ from the menu.
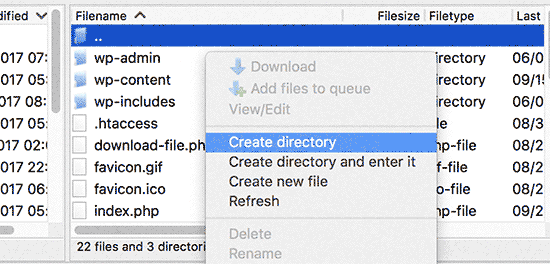
You need to be careful when choosing the name for your subdirectory. This will be part of your new WordPress site’s URL and what your users will type in their browsers to reach this website.
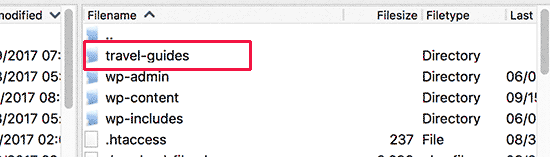
For example, if you name this directory travel-guides then your WordPress website’s address will be:
http://example.com/travel-guides/
Step 2. Upload WordPress Files
Your newly created subdirectory is empty at the moment. Let’s change that by uploading WordPress files.
First you need to visit WordPress.org website and click on the download button.
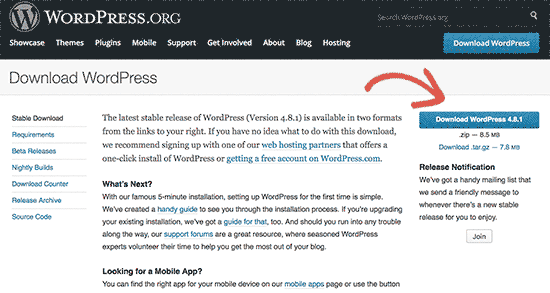
Your browser will now download the zip file containing the latest WordPress software to your computer.
After downloading the file, you need to select and extract it. Mac users can double click the file to extract it and Windows users need to right click and then select ‘Extract All’.
After extracting the zip file, you will see ‘wordpress’ folder containing all the WordPress files.
Now let’s upload these files to your new subdirectory.
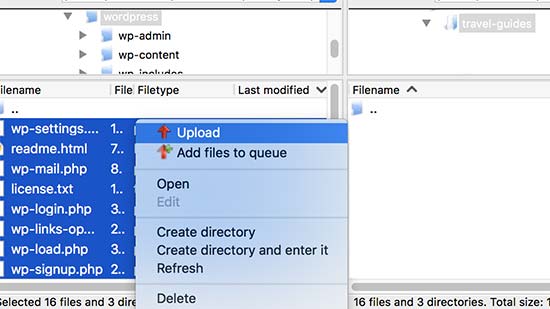
Connect to your website using a FTP client and go to the subdirectory you created in the first step.
In the local files panel of your FTP client, go to to the WordPress folder you just extracted.
Select all files in the WordPress folder and then upload them to your new subdirectory.
Step 3. Create New Database
WordPress stores all your content in a database. You need to create a new database to use with your new WordPress site installed in a subdirectory.
First, you need to login to the cPanel dashboard of your WordPress hosting account. Click on ‘MySQL Databases’ under the databases section.
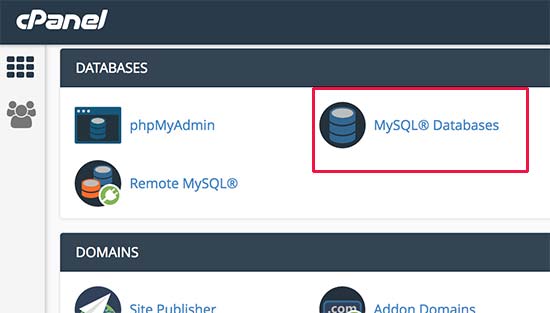
On the next screen, you need to provide a name for your new database and then click on ‘Create Database’ button to continue.
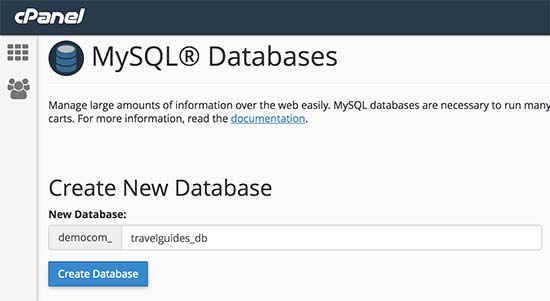
Your cPanel dashboard will now create the new MySQL database. In order to use this database you need to create a MySQL username.
Scroll down to MySQL Users section and provide a new username and password. Click on ‘Create User’ button to continue.
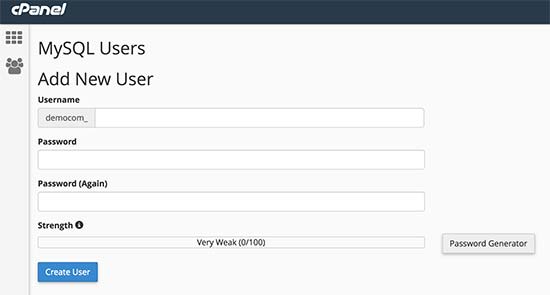
Next, you need to give this newly created user privileges to work on the database you created earlier.
Scroll down to ‘Add user to database’ section. Select your MySQL username and then select your newly created database.
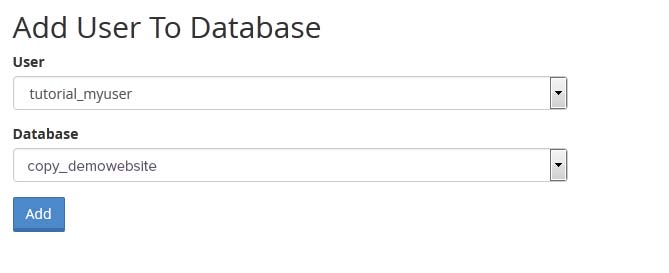
Click on Add button to continue.
Cpanel will now grant the MySQL user full privileges on your newly created database.
Step 4. Install WordPress
Now that everything is in place, you can go ahead and install WordPress. Simply visit the directory you created earlier in a web browser by typing the URL like this:
http://example.com/your-subdirectory-name/
This will bring up the WordPress installation wizard. First you need to select the language for your WordPress website and click on the continue button.
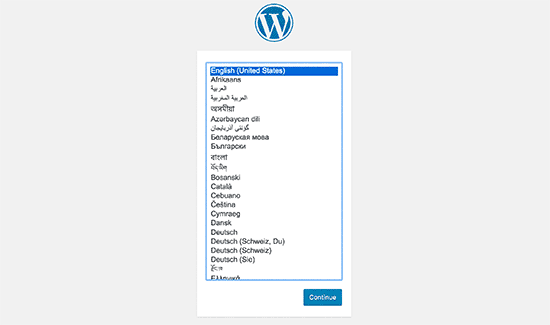
Next, you will be asked to provide your WordPress database name, database username, password, and host. Enter the database details and click on the submit button.
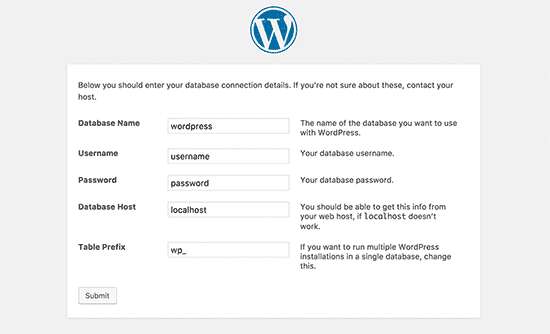
WordPress will now connect to your database and you will see a success message like this:
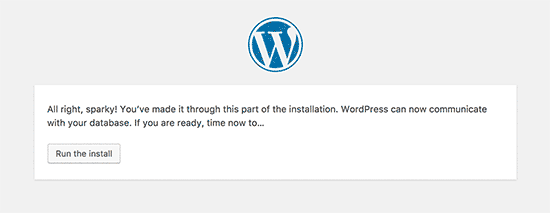
Click on ‘Run the install’ button to continue.
On the next screen, you will be asked to provide a title for your website and choose an admin username, password, and email address.
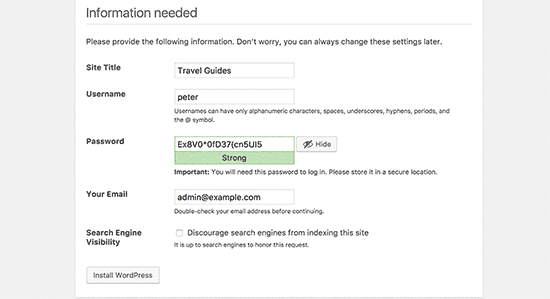
After entering your website details, click on ‘Run install’ button to continue.
WordPress will now set up your website and will show you a success message:
You can now go ahead and login to your new WordPress website installed in the subdirectory.
Step 5. Fix Permalinks
If you have a separate WordPress install in the root directory, then the .htaccess files of your subdirectory will cause conflict. This will result in 404 errors on your website.
To solve this, you need to edit the .htaccess file in your subdirectory WordPress install. Replace the code inside your .htaccess file with the following code:
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /your-subdirectory/
RewriteRule ^index.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /your-subdirectory/index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPress
Don’t forget to replace /your-subdirectory/ with your own subdirectory name.
- Sale
Connect 365/7/24 Hourly Support
Original price was: $120.00.$99.00Current price is: $99.00. - Sale
Connect Auto-Pilot for WordPress Content Management
Original price was: $599.00.$499.00Current price is: $499.00. - Sale
%22%20transform%3D%22translate(1.8%201.8)%20scale(3.63281)%22%20fill-opacity%3D%22.5%22%3E%3Cpath%20fill%3D%22%23c2ffee%22%20d%3D%22M204.4%20130.6l1.2%2072-158%202.8-1.2-72z%22%2F%3E%3Cellipse%20fill%3D%22%23c4ffef%22%20cx%3D%22122%22%20cy%3D%2272%22%20rx%3D%2283%22%20ry%3D%2235%22%2F%3E%3Cellipse%20fill%3D%22%23beffea%22%20cx%3D%2265%22%20cy%3D%22126%22%20rx%3D%2235%22%20ry%3D%2256%22%2F%3E%3Cellipse%20fill%3D%22%2388ccb5%22%20rx%3D%221%22%20ry%3D%221%22%20transform%3D%22matrix(51.92988%20-137.38378%2059.61857%2022.5353%20255%20209.3)%22%2F%3E%3C%2Fg%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageConnect WordPress Maintenance Plans
$99.00 – $224.00






